
Pioneer in Industrial Automations Services | Enriched With Quality in Time
INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERS (INDIA), having latest Technology CNC Winding & Forming machines for Re-winding purpose, and also having Latest testing equipments.
INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERS (INDIA), having Rewinding facility up-to 1200 MW Turbo Alternators.
Turbo generator is a turbine directly connected to electrical generators for the generation of electric power. These machines are the largest energy converters found in the world. They can also be used as auxiliary power units.
They are of 3 types namely:
1) Steam turbine generators
2) Gas turbine generators
3) Hydro turbine generators
The function of a turbo-generator is to convert rotational mechanical energy into electrical energy. It can be configured with different prime movers such as a steam turbine, a gas turbine in single-cycle or combined-cycle arrangement.
An electric current is induced in a conductor in proportion to the rate of change in the lines of magnetic flux." Essentially this means that if there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field, then current will be generated in the conductor. The amount of current generated is proportional to the density of the magnetic field and the speed of the relative motion between the conductor and the magnetic field.
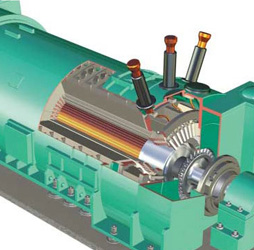
"An electric current is induced in a conductor in proportion to the rate of change in the lines of magnetic flux." Essentially this means that if there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field, then current will be generated in the conductor. The amount of current generated is proportional to the density of the magnetic field and the speed of the relative motion between the conductor and the magnetic field.
In a turbo-generator this principal manifests itself in a rotating magnetic field that generates current in stationary conductors (stator windings). The rotating magnetic field is produced in the rotor by a set of copper windings embedded in slots on the outside of the rotor body. DC current (excitation current) supplied to these windings through a set of slip rings or a brushless exciter creates an electromagnetic field that rotates with the rotor. As the turbine drives the generator rotor, this magnetic field cuts across the stator windings that are mounted in slots on the inside diameter of the stator core. The output from the stator windings is fed to a step-up transformer that adapts the power to grid voltage.